Summary
This paper explains how LiFi, a radical new technology, brings wireless connectivity in manufacturing where speed, stability, and cyber-security matter.
After well over a decade of research and development, LiFi is finally ready, and we are the leader! We are the first, and only LiFi provider in major defense and aerospace applications and we are now bringing it as the right wireless connectivity for all the demanding needs of multiple domains such as the financial sector, healthcare, enterprise, Esports, gaming, and education.
Wireless: the usage crisis
The importance of wireless technology lies in its ability to offer mobility, connectivity, and accessibility for multiple domains, ranging from industrial activities to esport and healthcare. These capabilities have become vital in our interconnected world as evidenced by the 19.5 billion WiFi connected devices in 2023. This number continues to grow, and with no end in sight.
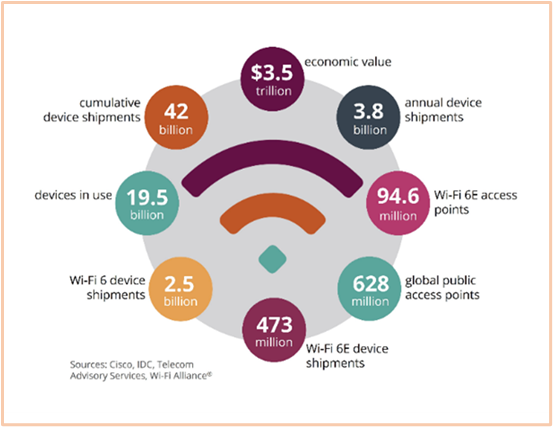
The exponential growth of WiFi usage has inevitably exposed several shortcomings within the technology landscape. These issues arise from a multitude of factors including over-usage, piracy, and interferences, which stem from the challenges of a limited RF spectrum shared between numerous usages. Notably, the spectrum utilized by WiFi interfaces with other major technologies (satellite, radars, WLAN, cellular phones, digital TV and radio, IoT, smart buildings…), encompassing a wide range of radio frequencies. For instance, while Zigbee operates at 868MHz, WiFi 7 extends up to 6 GHz, exacerbating the potential for spectrum congestion and interference.
Recent wireless announcements (WiFi 7 with MU-MIMO, Multi-Link Operation, 320MHz channels, 4096 QAM…) may bring a temporary relief but not a permanent fix. RF spectrum sharing will cause interferences as usage grows, and communications that can be intercepted, can be tempered with.
In addition, RF communication is not compatible with, and in some cases, not permitted in certain environments such as aerospace, healthcare, and critical infrastructure facilities.
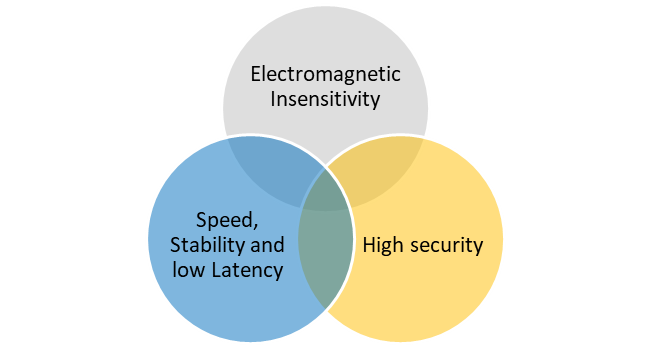
A radical innovation is needed for applications and specific areas that require speed, stability, resilience to hacking, and RF insensitivity.
LiFi: a solution for mission critical wireless
LiFi makes use of invisible light, with three immediate advantages.
- Because invisible light operates outside congested RF frequencies, it delivers superior stability, speed, and latency compared to WiFi, with zero interference
- For this same reason, LiFi can provide wireless communications in places where RF is prohibited because of other RF sensitive equipment.
- Finally, light does not cross walls; therefore, being a physical barrier to prevent signal interception, intrinsic immunity to crosstalk, and quasi-non-existent opportunities to hack or to jam.
in the industrial world, with characteristics as illustrated in the table below. While WiFi or 5G – with private 5G networks - remain acceptable wireless solutions for usages not reliant on security, performance, speed, or RF insensitivity, LiFi emerges as the preferred choice for various other scenarios
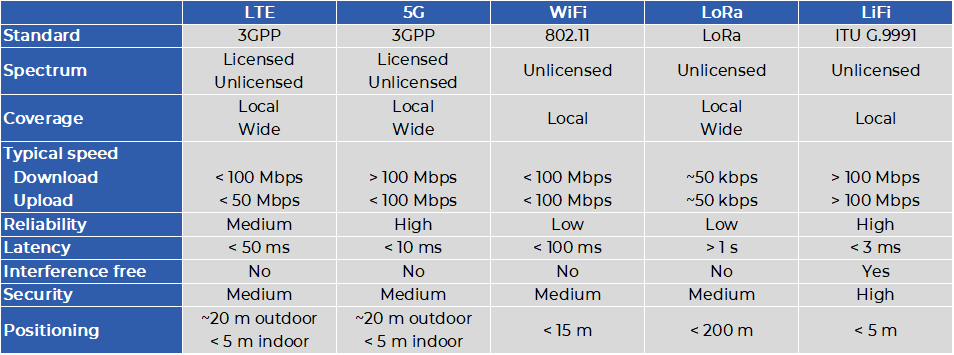
Comparison of existing wireless technologies
Manufacturing: a foundation of our global economy
Manufacturing is a wide and varied sector ranging from microbreweries to aerospace facilities and vehicle assembly lines. According to the World Bank, it accounts for roughly 16% of the world’s gross domestic product (GDP), being thus one of the foundations of our global economy.
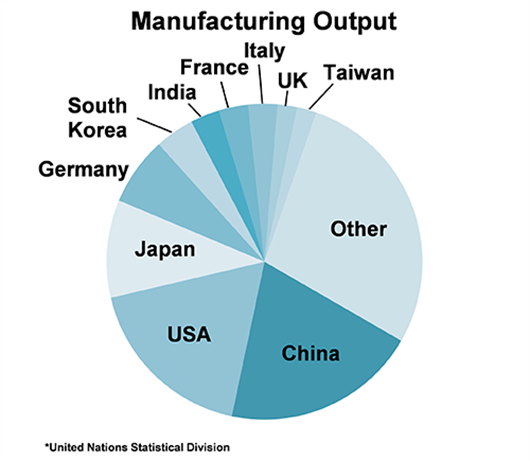
Moreover, manufacturing business is a fairly concentrated activity where China, the USA and Japan represent nearly half of the global manufacturing output.
To achieve the next level of productivity and stay competitive (for instance in the USA), manufacturers have to rely more and more on connected equipment: this approach, in line with the move to IoT and often coupled with AI (central and/or edge), is a part of what we usually call the Industry 4.0. Connectivity is thus fundamental, but can face several issues such as performance, reliability and security.
Security requirements for secure industrial automation and control systems (IACS) were first defined by the US International Society of Automation (ISA) with the ISA99 standards in 2002. They have been taken over in the ISA/IEC 62443 series of standards that are endorsed by the United Nations and recognized as a horizontal standard.
Several approaches are envisaged, one of them being the use of local/private 5G networks. While bringing strong advantages, 5G still relies on RF, which disqualifies it from the point of view of
- Security: as any RF solution, the signal remains easily detectable, then hackable and jammable from outside. Beyond the risk to have its data exposed, any manufacturing operations relying on 5G wireless connectivity could then be easily perturbated or even fully stopped.
- RF sensitivity: some industries, especially in the aerospace and telecommunication sectors, need to work in clean RF environment to produce, calibrate and test properly their production.
- Signal quality: factories are usually large areas with heavy metallic structures, preventing RF signal propagation, while light-based signal is not affected
On all these aspects, LiFi bring the solution that is expected by the manufacturers.
Manufacturing: a prime target for cyber-criminality
In 2022, manufacturing saw the highest share of cyberattacks among the leading industries worldwide. During this year, manufacturing companies encountered nearly a quarter of the total identified cyberattacks, showing the absolute need for having secure connectivity solutions.
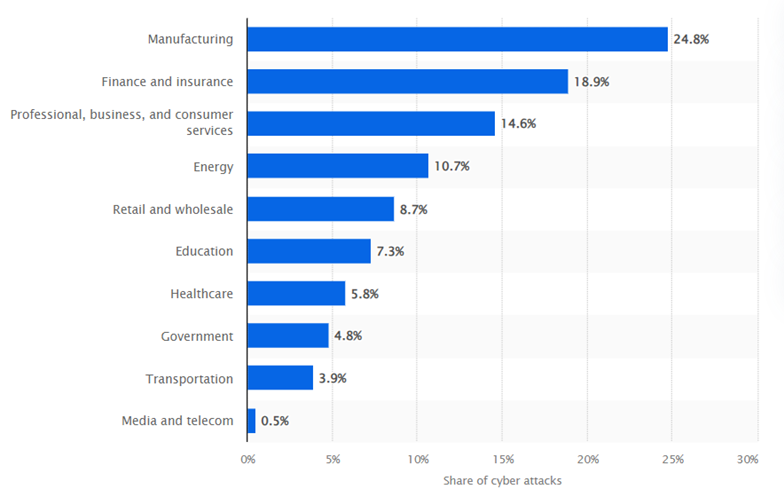
Distribution of cyber-attacks across worldwide industries in 2022 (Source: Statista 2024)
With a number of cyber-attacks that increased every year since 2020 in the USA
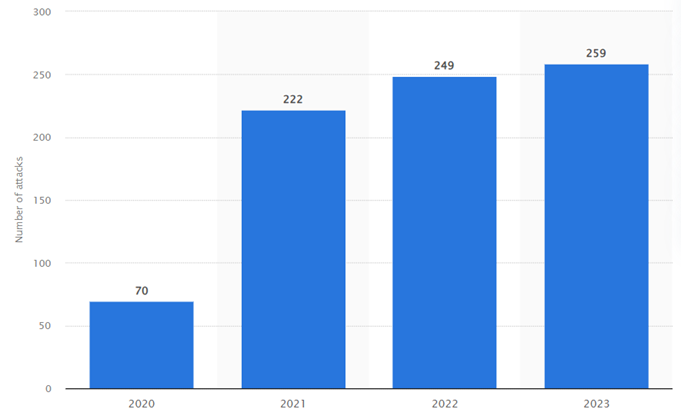
US number of data violation in manufacturing sector 2020-2023 (Source: Statista 2024)
The Manufacturing use cases
1. Equipment Monitoring and Maintenance

Connecting manufacturing equipment allows for precise monitoring of the performance, fast adaptation of the parameters depending on the product to manufacture and an efficient equipment predictive maintenance. Globally, the aim is to increase the OEE (Overall Equipment Efficiency), to maximize the ROI.
Wireless connectivity is not a priority but can be required for workshops that require flexibility and fast reconfiguration depending on the production plan. Stability and reliability are key as the equipment have usually a OEE above 85%.
2. Autonomous Mobile Robots

Autonomous robots are more and more used in warehouses, for both move in and move out operations. For many years autonomous robots have been installed for delivering the components to the manufacturing lines but using traditional methods such as magnetic strips or beacon guidance. Modern robots are now connected and navigate safely using Lidar sensors, 3D cameras and mapping software. Their performance depends on real-time data they receive, and they can thus improve workers safety and handle materials more accurately, eliminating up to 30% of typical scrap. They permit forklift operators being freed up to do other tasks in the factory.
Wireless connectivity is of course mandatory. The key characteristics are reliability, real-time positioning and low latency, three domains where LiFi is the best solution.
3. Collaborative Robots

Collaborative robots, aka Cobots, work side by side with operators to conduct different kinds of operations such as drilling, assembling, moving heavy parts or inspecting quality of products. One of the major requests for Cobots is the flexibility, meaning programming through SW download and the possibility to be moved very easily from one working place to another.
The major requirements of the wireless connectivity are the low latency and the reliability. Easy positioning is also key to help having an optimized management of the park of Cobots. Here again LiFi offers the best possible performance versus other wireless technologies.
4. Work instructions and Augmented Reality

Assembly quality and efficiency relies on assembly instructions that are carefully prepared by the industrialization teams. These instructions require frequent updates, either because of product modifications or simply because of the change in the production planning. Moreover, the worker might require additional information during his work, especially when a production issue happens. Having online information, and especially through AR solutions, makes his/her work easier, preventing production halt and increasing product quality and production efficiency. AR solutions can make use of connected tablets or connected AR helmets/glasses.
Low latency is key for such application, as the data that is displayed must be real-time synchronized with the worker’s movement and the product position.
Conclusion
Thanks to its use of light instead of RF transmission, LiFi brings the following unique and extremely important properties for wireless transmission for manufacturing activities:
- An absolute unsensitivity to RF, allowing its use close to any RF sensitive equipment, especially for the manufacturing and testing of telecom or radar equipment.
- A physical security for data transmission, that can secure all the manufacturing operations and the IP involved in the manufacturing process, but also prevents any signal jam that could literally stop a running production or damage equipment and harm people.
- The lowest latency, permitting then a precise real-time monitoring of running equipment, real-time behavior of autonomous robots and cobots, and perfect data visualization for AR- assisted production.
In addition, 5G, often promoted for Industry 4.0, requires a specific infrastructure: its deployment and operation can then be expensive and need specific telecom expertise that the manufacturer’s IT teams will not have. On the other hand, LiFi deployment is a seamless change from wired or WiFi last meters to LiFi access points and antennas. Moreover, once installed, LiFi subnetworks are managed exactly as other subnetworks are. LiFi then perfectly fits any IT team expertise.